 淺談android中的適配器模式
時間:2018-09-26 來源:未知
淺談android中的適配器模式
時間:2018-09-26 來源:未知
引言:在長期的android教學中,不難發現ListView是一個讓學生十分頭痛的組件,原因很簡單,這里有個適配器的概念,對于學生來講是一個從未涉及的新的領域,那么我們就通過這邊文章來初識一下軟件設計模式中的適配器模式。
1.適配器模式的定義:
Convert the interface of a class into another interface clients expect. Adapter lets classes work together that couldn't otherwise because of incompatile interfaces.
將一個類的接口變成客戶端所期待的另一中接口,從而使原本因接口不匹配而無法在一起工作的兩個類能夠在一起工作。
其中用到適配器模式的經典例子就是插座匹配問題,直接給圖:
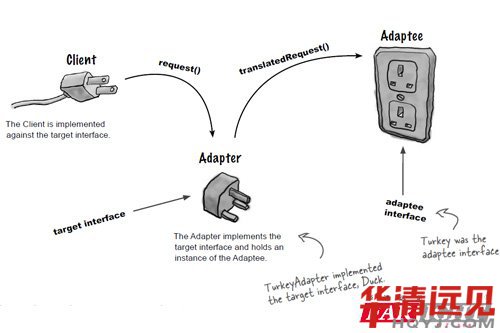
2.適配器模式的分類:
適配器模式主要分為兩種:類適配器和對象適配器
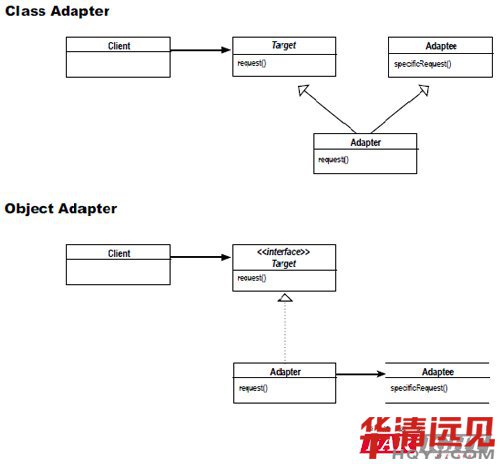
如上圖所示(截取自《Head First Design Patterns》一書),主要包括三個部分:
1) Target目標角色。該角色定義把其他類轉換為我們的期待接口。
2) Adaptee源角色。就是原始的類和接口對象,它是已經存在的,只是不符合現有的要求,而需要利用適配器角色的包裝。
3) Adapter適配器角色。適配器模式的核心角色,其它兩個角色都是已經存在的角色,而適配器角色是需要新建立的,它的職責非常簡單;把源角色轉換為目標角色;通過繼承或是組合的方式。
3.適配器模式的優勢:
1)適配器模式可以讓兩個沒有任何關系的類在一起運行,只要適配器這個角色能夠搞定它們。
2)增加了類的通透性,我們訪問的Target目標角色,但是具體的實現都委托給了源角色,而這些對高層次模塊是透明的,也是它不需要關心得。
3)調高了類的復用性和靈活性非常好。如果覺得適配器不夠好,只要修改適配器就行,其它的代碼都不用修改,適配器就是一個靈活的構件,想用就用。
4.適配器模式在android源碼中的應用:
在Android源碼中,ListView中用到的就是適配器模式。ListView用于顯示列表數據,但列表數據形式多種多樣(),為了處理和顯示不同的數據,我們需要對應的適配器作為橋梁。
在ListView中有一個變量ListAdapter mAdapter;是顯示在view試圖上的數據:
/**
* The adapter containing the data to be displayed by this view
*/
ListAdapter mAdapter;
在ListAdapter中定義了所需要的接口函數:
package android.widget;
/**
* Extended {@link Adapter} that is the bridge between a {@link ListView}
* and the data that backs the list. Frequently that data comes from a Cursor,
* but that is not
* required. The ListView can display any data provided that it is wrapped in a
* ListAdapter.
*/public interface ListAdapter extends Adapter {
/**
* Indicates whether all the items in this adapter are enabled. If the
* value returned by this method changes over time, there is no guarantee
* it will take effect. If true, it means all items are selectable and
* clickable (there is no separator.)
*
* @return True if all items are enabled, false otherwise.
*
* @see #isEnabled(int)
*/
public boolean areAllItemsEnabled();
/**
* Returns true if the item at the specified position is not a separator.
* (A separator is a non-selectable, non-clickable item).
*
* The result is unspecified if position is invalid. An {@link ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException}
* should be thrown in that case for fast failure.
*
* @param position Index of the item
*
* @return True if the item is not a separator
*
* @see #areAllItemsEnabled()
*/
boolean isEnabled(int position);
}
它是繼承自Adapter:
其中Adapter定義了getCount()、getItemViewType(int position)等接口函數。
此時的ListAdapter就是一個Target目標角色,而我們的ListView就是一個Client。因此為了適配和顯示一些數據,如Cursor等,所以就需要相應的適配器CursorAdapter,代碼如下:
public abstract class CursorAdapter extends BaseAdapter implements Filterable,
CursorFilter.CursorFilterClient {。。。
protected Cursor mCursor;
protected ChangeObserver mChangeObserver;
protected DataSetObserver mDataSetObserver;
protected CursorFilter mCursorFilter;
。。。
/**
* Returns the cursor.
* @return the cursor.
*/
public Cursor getCursor() {
return mCursor;
}
// 實現ListAdapter目標接口的getCount函數,通過返回源角色mCursor的方法getCount函數
/**
* @see android.widget.ListAdapter#getCount()
*/
public int getCount() {
if (mDataValid && mCursor != null) {
return mCursor.getCount();
} else {
return 0;
}
}
// 實現ListAdapter目標接口的getItem函數,通過返回源角色mCursor的方法moveToPosition函數
/**
* @see android.widget.ListAdapter#getItem(int)
*/
public Object getItem(int position) {
if (mDataValid && mCursor != null) {
mCursor.moveToPosition(position);
return mCursor;
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 實現ListAdapter目標接口的getItemId函數,通過返回源角色mCursor的方法getLong函數
/**
* @see android.widget.ListAdapter#getItemId(int)
*/
public long getItemId(int position) {
if (mDataValid && mCursor != null) {
if (mCursor.moveToPosition(position)) {
return mCursor.getLong(mRowIDColumn);
} else {
return 0;
}
} else {
return 0;
}
}
@Override
public boolean hasStableIds() {
return true;
}
其中源角色Cursor接口如下所示:
public interface Cursor {
。。。
/**
* Returns the numbers of rows in the cursor.
*
* @return the number of rows in the cursor.
*/
int getCount();
/**
* Returns the current position of the cursor in the row set.
* The value is zero-based. When the row set is first returned the cursor
* will be at positon -1, which is before the first row. After the
* last row is returned another call to next() will leave the cursor past
* the last entry, at a position of count().
*
* @return the current cursor position.
*/
int getPosition();
。。。
/**
* Move the cursor to an absolute position. The valid
* range of values is -1 <= position <= count.
*
*
This method will return true if the request destination was reachable,
* otherwise, it returns false.
*
* @param position the zero-based position to move to.
* @return whether the requested move fully succeeded.
*/
boolean moveToPosition(int position);
。。。
/**
* Returns the value of the requested column as a long.
*
*
The result and whether this method throws an exception when the
* column value is null, the column type is not an integral type, or the
* integer value is outside the range [Long.MIN_VALUE,
* Long.MAX_VALUE] is implementation-defined.
*
* @param columnIndex the zero-based index of the target column.
* @return the value of that column as a long.
*/
long getLong(int columnIndex);
。。。
}
這就將Cursor類型接口通過CursorAdapter適配器轉換成目標角色ListAdapter目標接口,繼而讓ListView使用,并展示。
以上就是android中關于ListView的適配器模式使用一些簡單分享,希望對大家學習ListView有所幫助。

